Aquaponics system showing its architectural implementation in the form of a planter wall within a building which connects its water to a fish pond to form a closed system.
Tuesday, February 23, 2016
Monday, February 22, 2016
Assignment 1.3 - Supatra Villegas
A speculative project, by incorporate an agriculture, and aquaculture and a method of desalination, the Solar Floating Farm could become an ideal proposal for food crisis issue today. These multi-scalar feedback loops show connections ranging from macro to micro levels, Within the Aquaponic cycle, there are secondary feedback loops; a Nitrogen cycle and a Photosynthesis cycle (on the plant). Energy from sunlight is the main factor for desalination and photosynthesis in both above and below water. The water from desalination can go to multiple feedback loops, for example: water to aquaponic system or it can go to human consumption.
Tuesday, February 9, 2016
Assignment 1.2 - Ana Cecilia Toledano
Aquaponic System
An Aquaponic System, which combines Aquaculture and Hydroponic Systems, has many inputs such as light, water, plants, fish, a medium such as gravel for the plants to live in, electricity, water and oxygen. It involves many smaller systems or processes such as Nitrification and Mineralization in the growth bed; as well as a digestion process for the fish in the fish tanks.
Assignment 1.1 - Ana Cecilia Toledano
Aquaponics System
An Aquaponics System consists in a combination of a Hydroponic System and a Aquaculture System. It consists of growing plants in a medium through which water rich in nutrients flows. This water then goes to a fish tank, where fish use it as a medium to live in. As the fish eat and digest the food, they produce waste, which turns into ammonia and serves as fertilizar for the plants, which use the water with ammonia that comes from the fish tank. When the water goes to the bed, the process of nitrification occurs, and nitrogen is broken down in order to be absorbed by the plants. After this process, the water is now clean enough to return to the fish tank. The invisible which I made visible was the Nitrification process and the Digestion process, which together make up a Nitrogen Cycle.
Assignment 1.2 – Tong Xiao
Flooding Mangrove_Guard
Mangrove acts as the guard towards flooding.
One hand, it has respiration and photosynthesis cycle to provide the energy of trunk and leaves' growing above the water all the time. At the same time, it has aerobic respiration function through air holes, called lenticel of pneumatophores and desalination function through leaves and roots at the flooding time. All the above help mangrove grows, especially for the expansion of the roots network, which support mangroves standing in the flooding water and create the space for the new habitat for species.
On the other hand, the fallen leaves of mangrove would be eaten by crabs. After Fungi and Bacteria breaking down the leaves, the decomposed litter would be absorbed by small prawns and fish. The remaining particular organic matter could be the food for smaller crustaceans, which are fed on by larger fish. Eventually, the organic matter of mangrove litter would be recycled through root system by mangrove itself.
That's to say, the characteristics of adaption to flooding turn the mangrove to the cradle of coastal ecosystem. New species speed up the loop of nutrients cycle which expand the growing of root systems, which provides the habit space back for the species. It can be some kind of meaning "metabolism".
Ref:
Adaptations
of Living Things\ http://wonders-of-the-wetlands.weebly.com/adaptations.html
Basic
Concepts in Environment, Agriculture and Natural Resources Management: An
Information Kit (International Institute for Rural Reconstruction (IIRR))\ http://www.nzdl.org/gsdlmod?e=d-00000-00---off-0envl--00-0----0-10-0---0---0direct-10---4-------0-1l--11-zhZz-tr-50---20-preferences---10-0-1-00-0--4----0-0-11-10-0big5-00&cl=CL1.1&d=HASH0192c760fbf07f7d6fa34cb8>=2
ALL
ABOUT MANGROVES\ http://www.bmrg.org.au/files/9014/0721/9454/MarvellousMangoveAustralia_1_AllAboutMangroves.pdf
Assignment 1.1 – Tong Xiao
Flooding Mangrove_Guard
This diagram shows the metabolic feedback loop based on the mangrove system.The mangrove system is a good typology ecosystem that can adapt coastal or estuary environment well. Either the chemistry process and physical process supports the surviving of mangroves in flooding climate. The mechanism of the leaves and root do help both in flooding and salty environment.
Thus the research based on the mangrove system focuses on the metabolism that
do adapt the flooding.
Assignment 1.2 - Tanjia Nabila
Building on the feedback loop, this phase focuses on the two different scenerios of the pneumatophore system: the 'before' or normal scenerio and the 'after' or high tide / coastal flooding scenerio of the mangrove and how it affects the pneumatophores. As the water sweeps in, some of the pneumatophores get submerged under water while others continue to provide the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the root network and trees, which would not have been possible without the pneumatophores. Local organisms, such as, crabs and worms, take shelter in and around the pneumatophores.
According to the given formula in the diagram, it has been proven that the higher the density of pneumatophores in a given area, the more oxygenated the soil condition will be, which in turn reduces the toxic build-up of chemicals in the soil.
Assignment 1.1 - Tanjia Nabila
Pneumatophores are aerial roots, usually found in tropical coastal swamps like mangroves. The trees use these protruding roots to receive extra supply of oxygen in an otherwise anaerobic condition of waterlogged soil of the mangroves. The surfaces of these roots are covered with lenticels (small pores) which absorb oxygen and nutrients from the atmosphere into its spongy tissues. The oxygen and nutrients then get transferred through the root network and to the tree. Pneumatophores additionally contribute to sustaining life in an inhospitable condition for not only the trees, but other animals and birds alike. They also strengthen the soil by holding onto it via their widespread network system.
Mitsch, William J., and James G. Gosselink. "Chapter 11 Mangrove Swamps." Wetlands. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2000. 335-76. Print.
Mitsch, William J., and James G. Gosselink. "Chapter 11 Mangrove Swamps." Wetlands. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2000. 335-76. Print.
Watson, Donald, and Michele Adams. Design for Flooding: Architecture, Landscape, and Urban Design for Resilience to Flooding and Climate Change. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2011. Print.
Assignment 1.1 – Afiul Khan
For people who live in areas prone to coastal flooding or areas waterlogged during the monsoon season, such as the southern riverine areas of Bangladesh, it is impossible to grow crops. The floating garden is a clever solution that employs the use of water hyacinth, which is collected to construct a raft. This is then covered with dirt, cow dung and compost in which vegetables can be planted. A new raft needs to be built every year, but the old one can be used as fertilizer during the dry season. The rafts are made from hyacinth, which is locally available. Compost is put on the surface of the raft and then the seeds planted into them. The rafts can be moved from place to place, therfore making it suitable for those that have temporarily or permanently lost their homes or land due to coastal flooding.
Assignment 1.2 – Afiul Khan
The Floating Garden Islands in larger scale and context act as a natural habitation letting birds, insects, fishes, bacteria, microbes and other organisms thrive amidst it. The floating island also acts as a two way buffer system that helps purify the water content as pollutants come in from the land and also acts as an inward wind and wave breaker
Monday, February 8, 2016
Assignment 1.2 - Yusi Yang
Different from assignment 1.1, I add an organic feedback loops in this atmosphere feedback loops diagram. On one hand, respiration and fossil fuels burning emits CO2 to atmosphere. On the other hand, plants assimilation can absorb CO2, while more atmospheric CO2 which cannot be absorbed go back to the earth again. The atmospheric CO2 in this feedback loop plays an important role in another positive feedback loop described in last assignment.
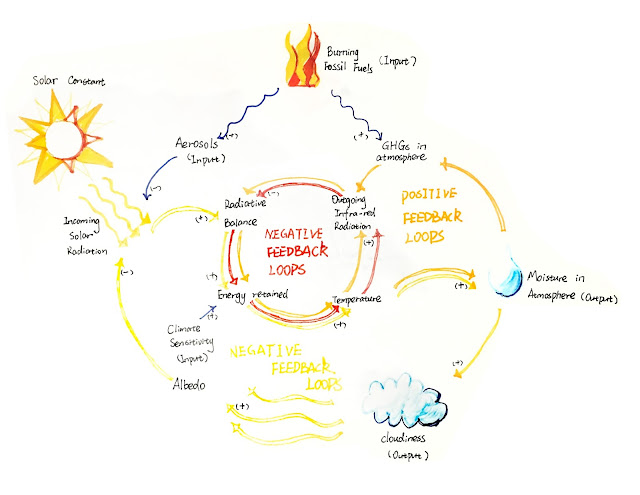
Assignment 1.1 - Yusi Yang
Temperature Feedback Loops
This diagram shows three feedback loops totally - one positive feedback loop and two negative feedback loops. Each feedback loop is marked in one same color. The inputs for these feedback loops are burning fossil fuels, solar constant, and climate sensitivity. The yellow feedback loop shows the increase of temperature could produce more moisture then more cloudiness. But more cloudiness will reduce incoming solar radiation and finally reduce temperature. On the other hand, the orange feedback loops is positive since the higher the temperature is, the more the GHGs could be preserved in the atmosphere, which could directly cause the increase of temperature. The third loop - the red one presents that the increasing of temperature could increase outgoing infra-red radiation and eventually increase the temperature again.
Assignment 1.1 Supatra Villegas
The Solar Floating Farm starts off from an idea of an aquaponic system and a solar desalination process. In this diagram, it shows fish that produce waste in the water, which then is pumped passing through a biofilter and then to the plant. During the process, ammonia from fish waste goes through microbes, like Nitrosomonas bacteria that metabolizes the ammonia into Nitrite. It then goes through Nitrobacter bacteria that turns Nitrite into Nitrate as shown in the Nitrogen cycle. Nitrate, which is a nutrient to the plant, then travels with water to plant beds, where another input/output is present. Plants absorb Nitrate and water as inputs, absorb the light from the sun and carbon dioxide from the air. Through photosynthesis, it then releases oxygen as an output and filters water back to the fish.
Assignment 1.2 Supatra Villegas
The Solar Floating Farm derives from the inspiration of an aquaponic system, and aquaculture and a method of desalination. These multi-scalar feedback loops show connections ranging from macro to micro levels, Within the Aqauponic cycle, there are secondary feedback loops; a Nitrogen cycle and a Photosynthesis cycle (on the plant). Energy from sunlight is the main factor for desalination and photosynthesis in both above and below water.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Blog Archive
-
▼
2016
(59)
-
▼
February
(22)
- Assignment 3 - Ana C. Toledano
- Assignment 1.3 – Andreas Theodoridis
- Assignment 1.3 – Tong Xiao
- Assignment 1.3 - Yusi Yang
- Assignment 1.3 Boxiao Liu
- Assignment 1.3 - Supatra Villegas
- Assignment 1.1 – Andreas Theodoridis
- Assignment 1.2 – Andreas Theodoridis
- Assignment 1.2 - Ana Cecilia Toledano
- Assignment 1.1 - Ana Cecilia Toledano
- Assignment 1.2 – Tong Xiao
- Assignment 1.1 – Tong Xiao
- Assignment 1.2-Boxiao Liu
- Assignment 1.1-Boxiao Liu
- Assignment 1.2 - Tanjia Nabila
- Assignment 1.1 - Tanjia Nabila
- Assignment 1.1 – Afiul Khan
- Assignment 1.2 – Afiul Khan
- Assignment 1.2 - Yusi Yang
- Assignment 1.1 - Yusi Yang
- Assignment 1.1 Supatra Villegas
- Assignment 1.2 Supatra Villegas
-
▼
February
(22)